June 10, 2025
Kymeta’s Breakthrough Multi-Band Antenna Redefines Connectivity
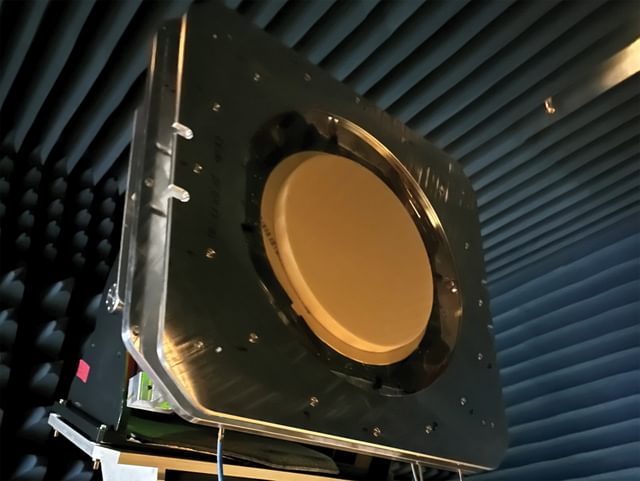
Kymeta achieves multi-band connectivity with four concurrent beams in Ku- and Ka-band frequencies with a single antenna aperture
Read more
Why Kymeta
The world of satellite connectivity is complex, but your solution doesn’t have to be. See how Kymeta makes it easy to get connected.

Applications



Products & Services


Designed for the US DoD and government agencies, the Osprey u8 is our most robust product — battle-tested and ready for action on land or at sea.

Able to switch dynamically between LEO and GEO satellite networks, the Goshawk u8 terminal is ready to provide on-the-go communications right out of the box.
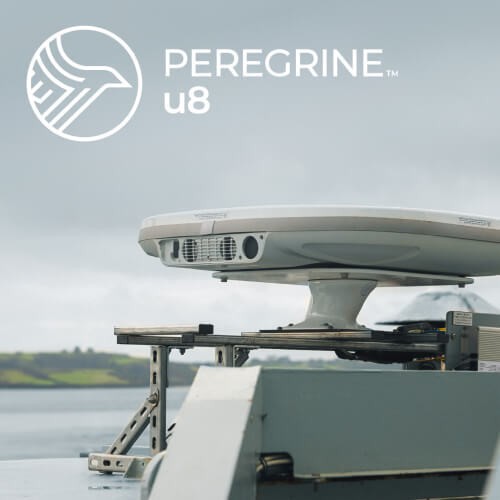

The Peregrine u8 is ideal for maritime connectivity, whether it’s commercial freight and fishing, or premier pleasure craft.
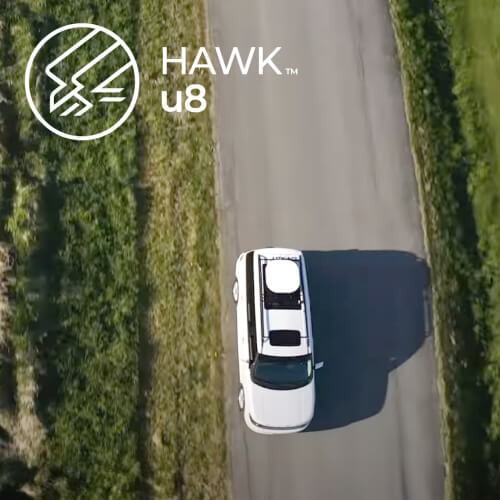

The Hawk u8 is an economical solution that can be preconfigured to work with either LEO or GEO satellite networks.
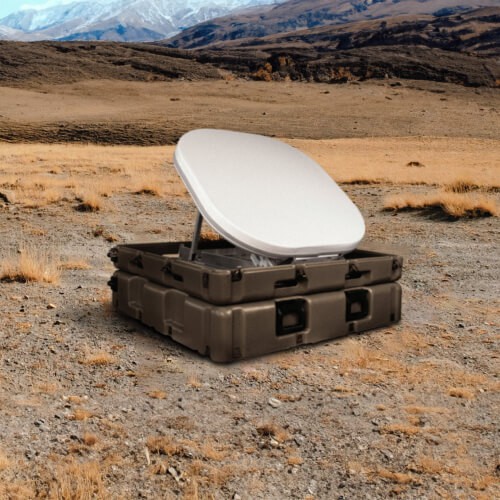

Learn about the range of u8 accessories from power supplies, to mounting and shipping solutions.


GEO satellite networks provide a stable connection thanks to their high vantage point above the earth. We offer GEO connectivity tailored to flat-panel antennas, including plans that include TRANSEC access.
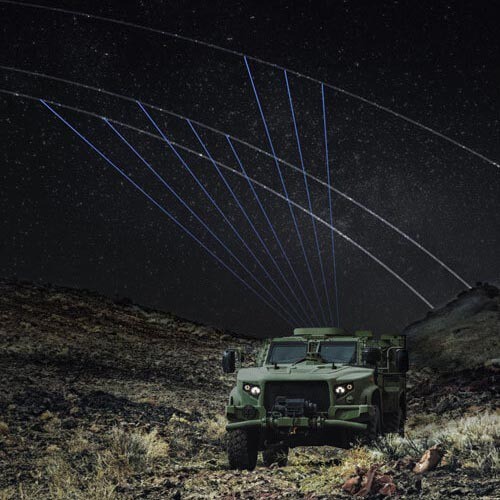

Our U.S. DoD bundle provides access and easy management of Ku GEO, Eutelsat OneWeb LEO, TRANSEC, and 4G LTE, plus the ability to manage many terminals in a single plan.
Support
Find key learning resources and information about the Kymeta Access app, plus training options and warranties.

About us
Learn about our company, and the exceptional people who are building the next generation of satellite connectivity.


Kymeta was recently featured in a report published in the IEEE Journal of Microwaves. The report reviews the current state of electronically steerable antennas for terrestrial and non-terrestrial communication systems and how they can support the rollout of 5G networks and how people and businesses reliably use 5G-powered services.
Within this piece, the potential benefits and limitations of the most relevant technologies are contrasted and put into context with recent system architectures for adaptive beamforming. Their operating principles, experimental implementation, and achievements providing advanced capabilities are discussed throughout. The authors placed emphasis on the review of direct radiating arrays, quasi-optical antenna configurations, and metasurface-based antennas as well.
The development and growth of 5G has transformed modern telecommunication systems and its impact on our day-to-day lives cannot be understated. The key drivers of 5G’s impact are rooted in the need for enhanced mobile broadband, ultra-reliable and low latency communications, and massive machine type communications, which are driving technological advancements across all segments of the network service ecosystem.
As 5G’s expansion is directly correlated with technological advancements in satellite and antenna technology, this paper presents an extensive overview of electronically steerable antennas for a plurality of point-to-point/- multipoint communication applications supporting 5G-powered services in the future. Subsequently, the current key technologies and components for realizing these reconfigurable antenna systems are reviewed highlighting their pros and cons in terms of integration, miniaturization, scalability, and RF performance.
In order to provide the reader with the latest technical advances in direct radiating arrays, various implementations of array elements as well as active antenna modules and systems were subject of this contribution, including Kymeta’s holographic antenna for Ku-band SatCom user terminals and metamaterials innovations.
Because holographic antennas with their subwavelength sized unit cells actually exacerbate the requirements on the integration of electronic components, significant efforts have also been devoted to the use of liquid crystals as a tunable dielectric. By leveraging flat panel display manufacturing techniques for high-volume production, Kymeta developed this LC-based holographic antenna for Ku-band SatCom user terminals. The radial aperture of the metasurface antenna consists of interleaved TX and RX elements which are specifically distributed to maintain full polarization control, but also to enhance the isolation between both communication directions while operating in full duplex.
To view the full paper, click here.
News & Insights

Kymeta products and services are available directly from us and through authorized reseller partners. Our sales team will help you understand your product and network configuration options, and answer any questions you have, then connect you with an authorized reseller partner to make your purchase.
Contact usWe offer Kymeta Insider, a general newsletter, as well as a dedicated newsletter for the Defense community.